Large Language Models (LLMs) are powerful but prone to hallucinations—generating incorrect or irrelevant information. Here’s how to reduce these hallucinations and improve the reliability of your AI.
Understand LLM Limitations
Before diving into practical tips, let's set out some simplified context to understand why hallucinations occur.
LLMs like GPT-4 are trained on vast datasets, storing patterns as vectors. For instance, the words "cat" and "dog" are likely to be close together in the vector space because they share many semantic similarities. Both are animals and mammals, which causes their vectors to be similar, but not exactly the same.
Here’s a simplified example of vector embeddings for various words:
| Word | Vector Embedding |
|---|---|
| cat | [1.5, -0.4, 7.2, 19.6, 20.2] |
| dog | [1.7, -0.3, 6.9, 19.1, 21.1] |
| apple | [-5.2, 3.1, 0.2, 8.1, 3.5] |
| building | [60.1, -60.3, 10, -12.3, 9.2] |
| Query: fruit | [-5.1, 2.9, 0.8, 7.9, 3.1] |
Looking at these embeddings, "cat" and "dog" are much closer to each other than to "apple" or "building." Similarly, the query "fruit" is much closer to "apple" and "strawberry" than to "cat" or "dog," making them the top results for a "fruit" query.
This allows models to generate intelligent responses as a world model emerges through proximity of embeddings.
However, this process of querying embeddings is metaphorically closer to memory as opposed to reasoning. These results are ranked, and the top ranked result returned. When this is a 'close' vector match, you get an hallucination, as if the wrong 'memory' was retrieved. This is a partial explanation of why LLMs hallucinate and return strange responses.
Memory vs. Reasoning
We can see these limitations in practice by asking an LLM to complete a ARC-AGI benchmark task. This is a simple but novel task that resists memorization - each task is unique.
Try completing the task yourself - can you complete the pattern?
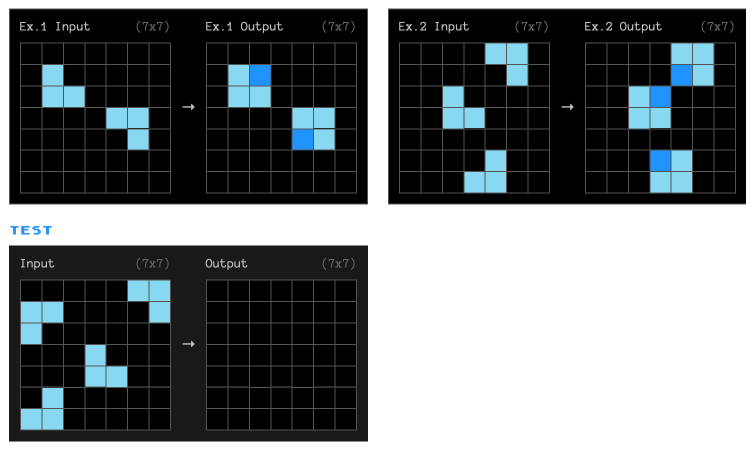
Whereas most humans can complete novel tasks like this with ease, LLMs struggle.
This does not mean that LLMs are useless, but that we should not expect novel reasoning and should tweak how we work with LLMs to maximise the practical applications of a memory-based approach.
Side note: I would love for this to change! If you disagree that LLMs rely upon memory, you could win $1M by solving an ARC-AGI benchmark task with AI.
Reducing Hallucinations
With this knowledge in mind, let's look into a few practical approaches I've found to reduce hallucinations when working with GPT-3, GPT-3.5, GPT-4 and GPT-4O.
Effective Prompting
Task Appropriateness
Before you write your prompt, determine if your task is suitable for current generation AI.
AI models struggle with tasks that require precise logic, deterministic outcomes, deal with novel visual/spatial elements or tasks that are uncommon in the training set.
A practical example is to generating a layout grid of arbitrary elements represented as a complex JSON object. As a complex visual task the model did not return visually pleasing results. Instead, I pre-defined sections with "slots" for relevant elements and selected these at random. AI was then used to fill the slots appropriately - a less visually demanding task.
Specific Directions
Using clear and precise language in your prompts is crucial to minimize ambiguity and improve the accuracy of LLM responses.
When prompts are vague or open-ended, the model may fill in gaps with incorrect or irrelevant information, leading to hallucinations.
Bad Example: "Write a short summary on AI healthcare."
Good Example: "Write a 300-word summary focusing on the main benefits of using AI in healthcare applications."
In the bad example, the prompt is too vague, leaving too much room for interpretation. The AI might generate a summary that misses key points or is too long/short for your purposes. The good example provides clear instructions on length and focus, leading to a more accurate and relevant output.
Include Examples
Providing examples of desired outputs helps the model understand your expectations and align its responses accordingly. Examples serve as a reference point, reducing the likelihood of hallucinations.
For instance, if you want the AI to generate a product description, show it a few samples of well-written descriptions. This contextualizes your request and helps the AI produce outputs that match your expectations.
Bad Example: "Describe this product."
Good Example: "Describe this product in a positive way using simple language that would be helpful to someone browsing our marketing website. Here are 2 examples of good product descriptions: [Example 1], [Example 2]."
Parameter Constraints
Explicitly stating what the AI should and shouldn’t do in your prompts can significantly improve the relevance and accuracy of responses.
For example, if you're asking for a summary, you might specify which details to include or exclude. This helps the model focus on the most relevant information and avoid unnecessary or incorrect content.
Bad Example: "Summarize the article."
Good Example: "Summarize the article. You MUST focus on the economic impacts and MUST NOT use technical jargon."
Direct Language
Avoid vague instructions in your prompts. Ambiguous language can confuse the model and lead to hallucinations. Instead, use direct and unambiguous language.
Bad Example: "Talk about the benefits."
Good Example: "As a list, give me three benefits of using renewable energy sources, focusing on environmental impact. Each must be at least 100 characters."
Provide Context
Offering background information or context in your prompts can significantly enhance the quality of AI responses. Context helps the model understand the nuances of your request and generate more accurate and relevant outputs. For example, if you're asking for an analysis, provide some background on the topic to guide the AI.
Bad Example: "Analyze the data."
Good Example: "Analyze the sales data from Q1 2023, focusing on trends and potential causes for the 15% decline in revenue compared to Q4 2022."
You may also wish to include other recent reports as an example of the type of analysis you are looking for. You could also include text from your marketing website for additional context.
Function Calling Best Practices
What is Function Calling?
Function calling lets you define functions for specific tasks. Instead of executing these functions directly, the model generates a JSON object with the necessary arguments for calling the function in your code. This approach confines the model to specific tasks, reducing the chances of hallucinations by keeping its actions within clear boundaries.
Schema-Based Approaches
Do not assume that the function call will always return a valid result. Use tools like Zod to validate inputs and outputs against a schema. For instance, when creating blog posts, you can validate the structure of the content object to ensure it includes required fields like title, author, and publish date. Upon an invalid response, you could throw an error, or return the error back to the conversation with the model, and prompt it appropriately e.g "The function call X returned an error for field Y".
Task-Specific Functions
Using simple, specific functions with clear return types is more effective than using generic ones. For example, you might ask a model to use a function that has multiple return types depending on the task. Try breaking these down into separate well-defined functions, with clear descriptions.
Lower Temperature Settings
Reducing randomness by lowering the temperature setting leads to more deterministic outputs. A lower temperature (e.g., 0.2) helps the model produce consistent and reliable responses, reducing the likelihood of hallucinations.
System Prompts
Including explicit instructions such as "You MUST only use the functions you have been provided with” within the system prompt guides the AI’s tool usage. If you do see repeat failures for certain fields in your schema, add explicit instructions to your system prompt. For example: "You MUST return either 'Kim', 'Jim', or 'Bob' for the 'name' field."
Summary
- Understand LLM limitations: LLMs store patterns but can't create new solutions for novel tasks.
- Effective Prompting: Use specific directions, include examples, set parameter constraints, use direct language, and provide context.
- Function Calling: Introduce and use function calling to control AI actions, validate with schemas, use task-specific functions, lower temperature settings, and guide with explicit system prompts.
Thanks for Reading!
I always appreciate feedback or suggestions for future blog posts. You can find me on LinkedIn or if you want to improve the article to help future readers, please feel free to submit a PR.
